Spleen Histology Labeled : White Pulp Wikipedia / It is a highly vascular haemopoietic organ situated in the left hypochondrium directly beneath the diaphragm, above the left kidney and descending colon, behind the fundus of the stomach and weighing about 150 gms in adult.
Spleen Histology Labeled : White Pulp Wikipedia / It is a highly vascular haemopoietic organ situated in the left hypochondrium directly beneath the diaphragm, above the left kidney and descending colon, behind the fundus of the stomach and weighing about 150 gms in adult.. It shows how the artery has a lymphoid sheath surrounding the artery, as it enters the spleen, with aggregations of secondary lymphoid tissue.this is where the regions of white pulp are found. The spleen is the largest organ of your lymphatic system, a subdivision of the immune system.its network of trabeculae, blood vessels and lymphoid tissue provides an environment in which white blood cells (lymphocytes) proliferate while old damaged red blood cells (erythrocytes) are recycled.although it may seem dispensable as it is possible to live without it, the spleen is constantly. In contrast to the other organs we have seen so far, the spleen is not arranged into cortex and medulla. Spleen this is a low power view of the spleen. The goal of this lab is to examine the organization of the major organs of the lymphatic system.
Thick connective tissue trabeculae of spleen #3. The spleen lies between the stomach and the diaphragm in the upper left hand side of the abdominal cavity. In dogs, the spleen increases in weight during the first 6 months of life (hoganesch and hahn, 2001). The spleen is the most important organ for lymphocyte recirculation. A knowledge of the functional anatomy of the spleen helps to interpret the effects of splenectomy and splenic transplantation.

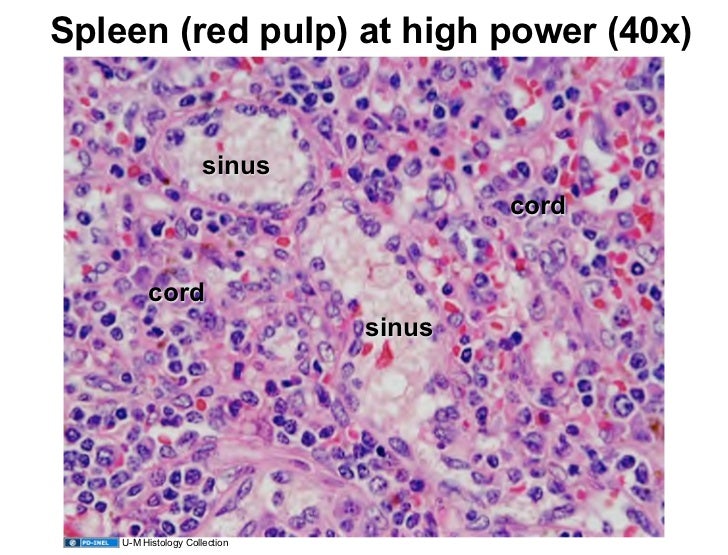
The arteries (arrow) are surrounded by white pulp (wp), which consists of lymphocytes and reticular connective tissue.
In dogs, the spleen increases in weight during the first 6 months of life (hoganesch and hahn, 2001). The goal of this lab is to examine the organization of the major organs of the lymphatic system. In this article we will discuss about the structure of. The spleen is the largest accumulation of lymphoid tissue in the body. These nodules contain the lymphocytes. Thick connective tissue trabeculae of spleen #3. Spleen this is a low power view of the spleen. Targeted mr contrast agents for the liver and spleen. It shows how the artery has a lymphoid sheath surrounding the artery, as it enters the spleen, with aggregations of secondary lymphoid tissue.this is where the regions of white pulp are found. Gross anatomy • the splenic artery and vein enter at the hilum. Where do i get my information from: By the end of the lab, you should be able to describe and distinguish lymph nodules, tonsil, lymph nodes, thymus, and spleen using the criteria given in the table below. Like the lymph nodes, the spleen is covered by an outer capsule that extends into the parenchyma as trabeculae.
The spleen has a unique location, embryological development and histological structure that differs significantly from other lymphoid organs. The spleen is an organ located in the upper left abdomen, and is roughly the size of a clenched fist. The spleen lies between the stomach and the diaphragm in the upper left hand side of the abdominal cavity. Branches before it reaches the spleen in dogs and cats. By the end of the lab, you should be able to describe and distinguish lymph nodules, tonsil, lymph nodes, thymus, and spleen using the criteria given in the table below.
These functions are carried out by the 2 main compartments of the spleen, the wh …
These nodules contain the lymphocytes. The spleen is the largest collection of lymphoid tissue in the body. Gross anatomy • the splenic artery and vein enter at the hilum. On the outer edge, note the presence of a capsule from which short trabeculae (containing a trabecular artery and trabecular vein) extend into the parenchyma. This diagrammatic representation of the spleen, should help you understand where red and white pulp come from. Thick dense connective tissue capsule #2. It is the largest lymphoid organ and thus the largest filter of blood in the human body. It shows how the artery has a lymphoid sheath surrounding the artery, as it enters the spleen, with aggregations of secondary lymphoid tissue.this is where the regions of white pulp are found. These trabeculae carry nerves, arteries and veins. The spleen is surrounded by a capsule of dense connective tissue from which emerge trabeculae, which divide the parenchyma, or splenic pulp, into incomplete compartments.large trabeculae originate at the hilum, on the medial surface of the spleen; Knowledge of splenic anatomy and technique, with efforts to save t … Targeted mr contrast agents for the liver and spleen. By the end of the lab, you should be able to describe and distinguish lymph nodules, tonsil, lymph nodes, thymus, and spleen using the criteria given in the table below.
Thick connective tissue trabeculae of spleen #3. Spleen histology slide (labeled) the spleen is a fist sized organ located in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen. Relative to the mouse spleen, the rat spleen has a larger and more uniform marginal zone (mz) and a more. Then as the artery loses its sheath and branches to form pencillar arteries, and sinusoids. Thick dense connective tissue capsule #2.

Branches before it reaches the spleen in dogs and cats.
An introduction to the histology of the spleen, as presented by the university of rochester pathology it program It shows how the artery has a lymphoid sheath surrounding the artery, as it enters the spleen, with aggregations of secondary lymphoid tissue.this is where the regions of white pulp are found. The anatomic entities involved with splenic surgery are presented. This diagrammatic representation of the spleen, should help you understand where red and white pulp come from. Innervation is purely sympathetic and nerve fibres travel with the artery into the spleen. The thymus is a primary lymphoid organ found within the superior mediatinum, behind the upper part of the sternum. The spleen is surrounded by a capsule of dense connective tissue from which emerge trabeculae, which divide the parenchyma, or splenic pulp, into incomplete compartments.large trabeculae originate at the hilum, on the medial surface of the spleen; Learn about its function, location in the body, and conditions that can affect the spleen. These functions are carried out by the 2 main compartments of the spleen, the wh … In this article we will discuss about the structure of. The spleen is the largest collection of lymphoid tissue in the body. Embedded within the red pulp are small white nodules called the white pulp. Intracellular particles and membrane defects of red cells are removed from the erythrocytes as they pass through the pulp cords of the red pulp.
Komentar
Posting Komentar